Peri-Urban
POTENTIAL THEMES & TOPICS
OVERVIEW
Spatial patterns
- Urban direct expansion
- Urban / rural fringe & gradient
- Counter-urbanization effect
- Urban agglomeration effect
Maps & Indicators
Functional dynamics
- Population growth & housing
- Technology & infrastructure
- Economy & employment
- Real estate & markets
Maps & Indicators
Social-eco dynamics
- Social demographics & lifestyle
- Environment & resources
- Policy & governance
- Culture & ethics
Maps & Indicators
Global-local dynamics
- Internal structures
- external interactions
- power dynamics
- challenges & conflicts
Maps & Indicators
Climate Risk
POTENTIAL THEMES & TOPICS
OVERVIEW
Climate change direct effects
- temperature
- precipitation, storm etc
- coastal effects
Maps & Indicators
Climate direct hazards & impacts
- wildfire, heatwave, drought,
- flood, storm, cyclone
- landslide, sea incursion etc,
Maps & Indicators
Indirect hazards & nexus effects
- water resources
- farming & forestry
- energy & resources
- ecosystems & microclimates
- critical infrastructure
Maps & Indicators
Peri-urban impacts on climate
- CO2 emissions from energy
- GHG emissions from land-use
- Land-use & forestry change
- Carbon storage
Maps & Indicators
Vulnerability
POTENTIAL THEMES & TOPICS
OVERVIEW
Physical sensitivity & capacity
- Soil & vegetation
- Topography & stability
- Settlement form & structure
Maps & Indicators
Techno-economic capacity
- technical & infrastructure
- Markets & value effects
- Employment & livelihoods
Maps & Indicators
Eco-social-cultural capacity
- Affluence / deprivation
- Education / communication
- Cultural issues
Maps & Indicators
Governance adaptive capacity
- Local government
- Public services & infrastructure
- Emergency services
- Civil & community
Maps & Indicators
Governance
POTENTIAL THEMES & TOPICS
OVERVIEW
Adaptive governance & institutions
- Public Sector
- Private Sector
- Civic Sector
- Citizens etc
Maps & Indicators
Informal governance & livelihood
- Informal land-use, settlements
- Corruption & nepotism
- Social innovation & enterprise
Maps & Indicators
System resilience & intelligence
- Social learning & collaboration
- Social co-creation & mobilization potential
- System transformation potential
Maps & Indicators
Synergistics
POTENTIAL THEMES & TOPICS
OVERVIEW
Systems / syndromes (present baselines)
- Main cross-cutting issues: e.g.
- Airport / port cities:
- Rural livelihoods:
- Informal development
Maps & Indicators
Scenarios (future possibilities)
- Critical themes: (STEEP): e.g.
- Social cohesion declines
- AI / IOT emerges
- Climate change accelerates
Maps & Indicators
Synergies (future ideas, opportunities)
- Potential ideas, connections, opportunities
Maps & Indicators
Strategies (present pathways, actions)
- Goals, objectives, targets for ways forward.
Maps & Indicators
Chennai region overview
Chennai region overview
Heavy-industries complex along ecologically-degraded coastline and scattered towns and farmlands
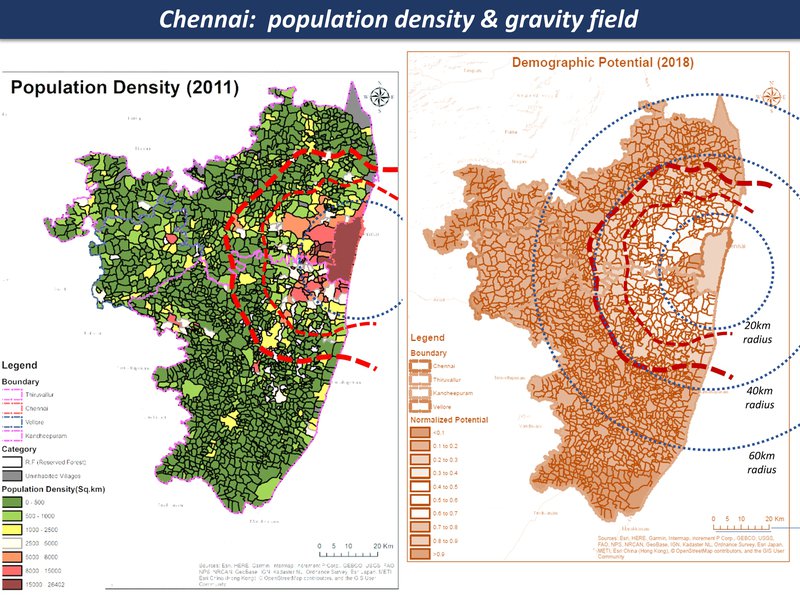
population density & gravity field
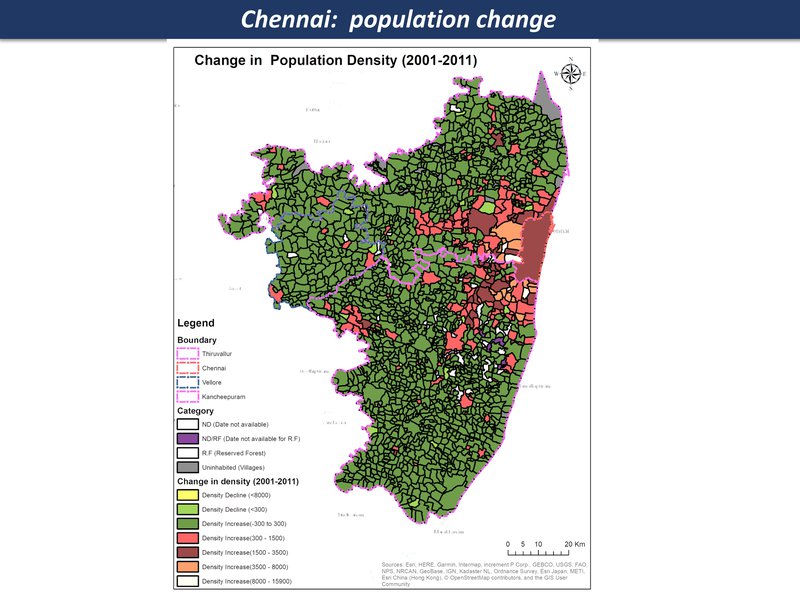
population density change
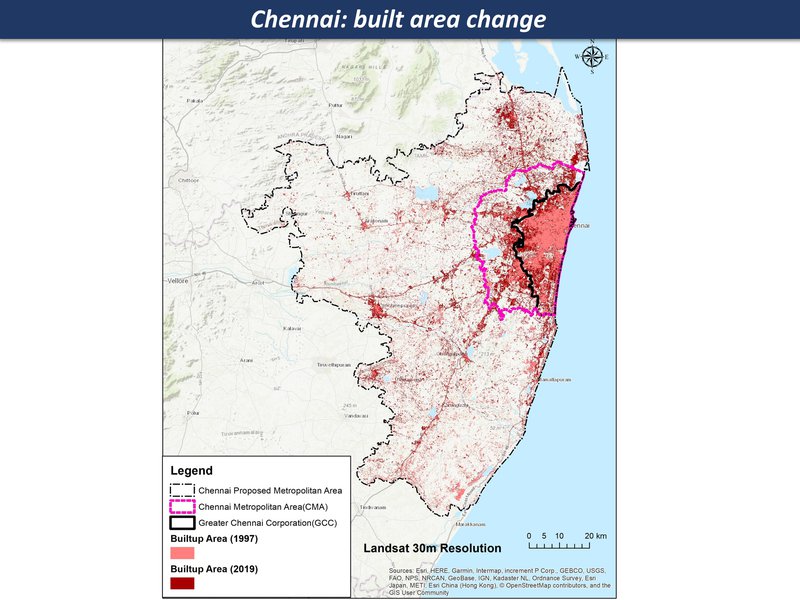
Chennai: built area change
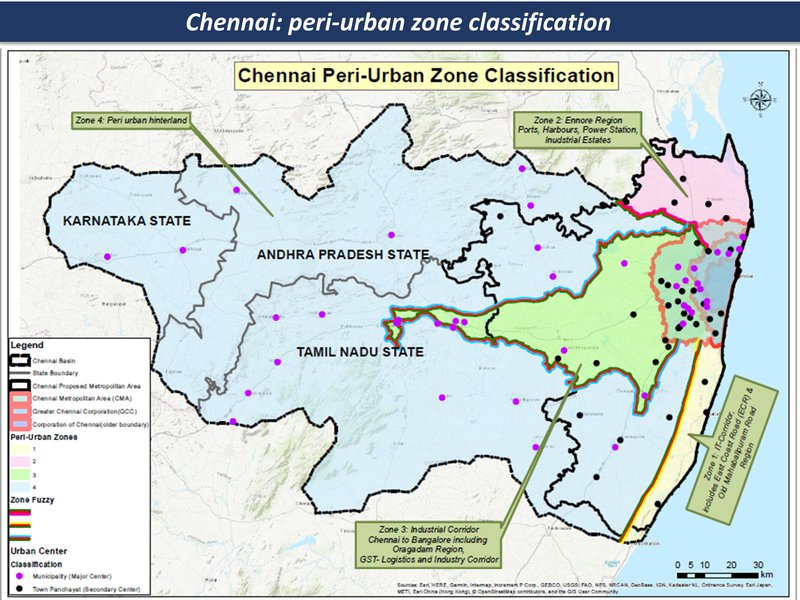
peri-urban zones
Chennai region overview
Chennai region overview
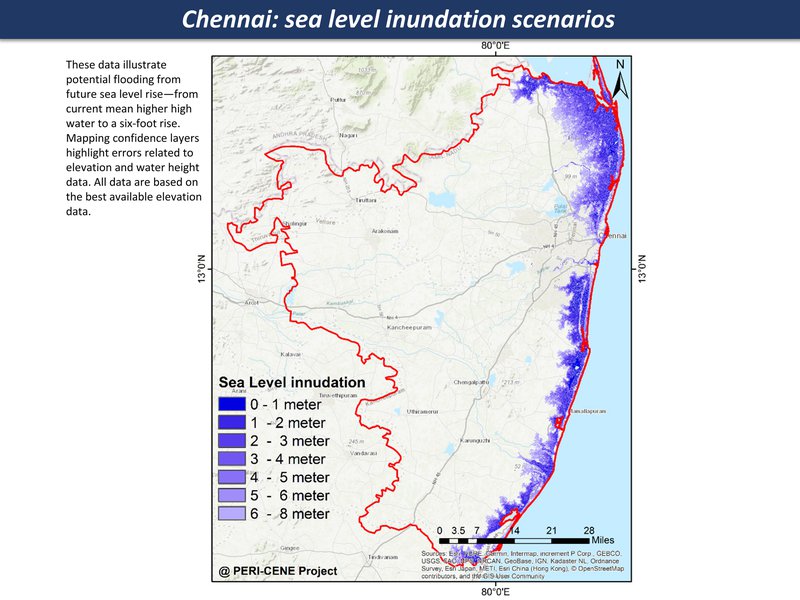
Sea level rise, increase in extreme events - storm, storm surges
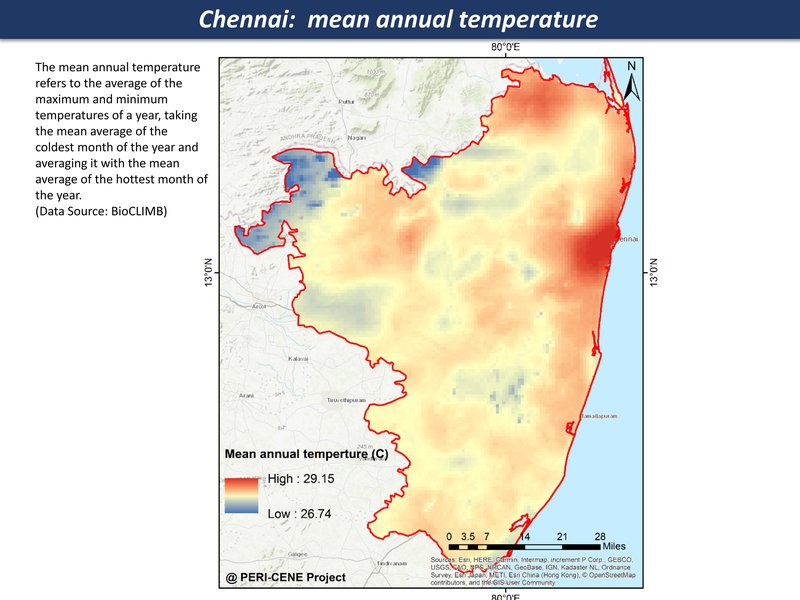
mean annual temperature
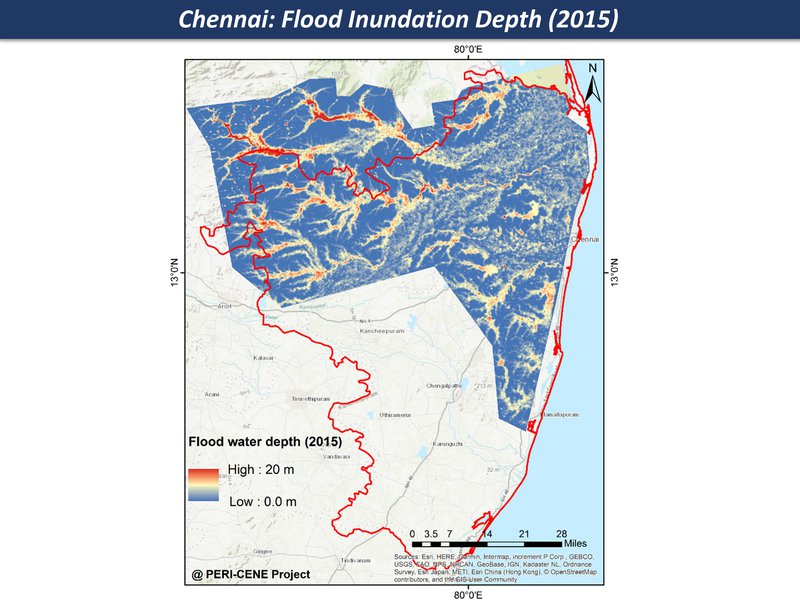
Flood inundation
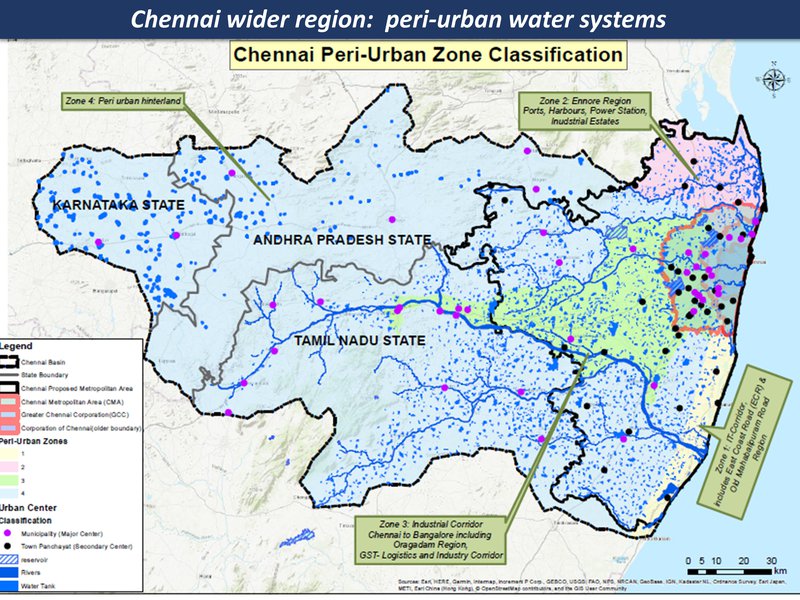
peri-urban water systems
Chennai region overview
Chennai region overview
urban eco-social-economic mix in some areas has growing vulnerability
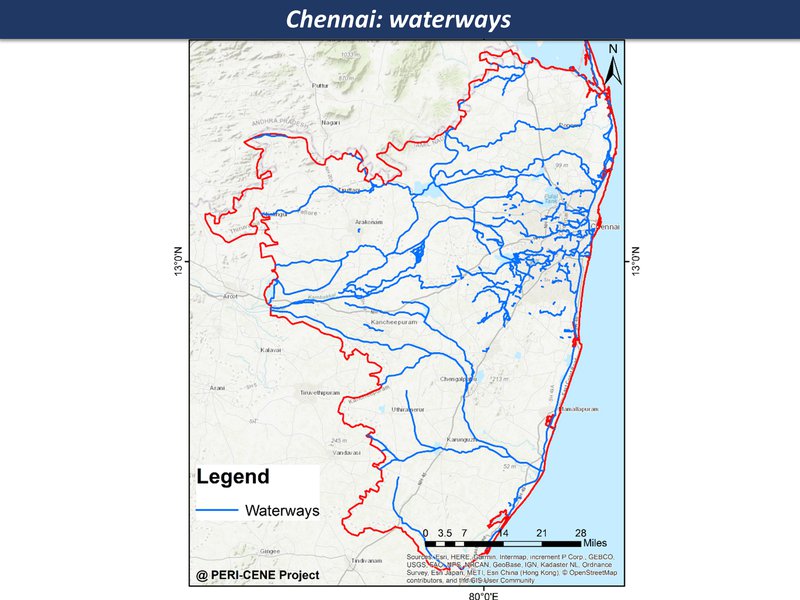
waterways
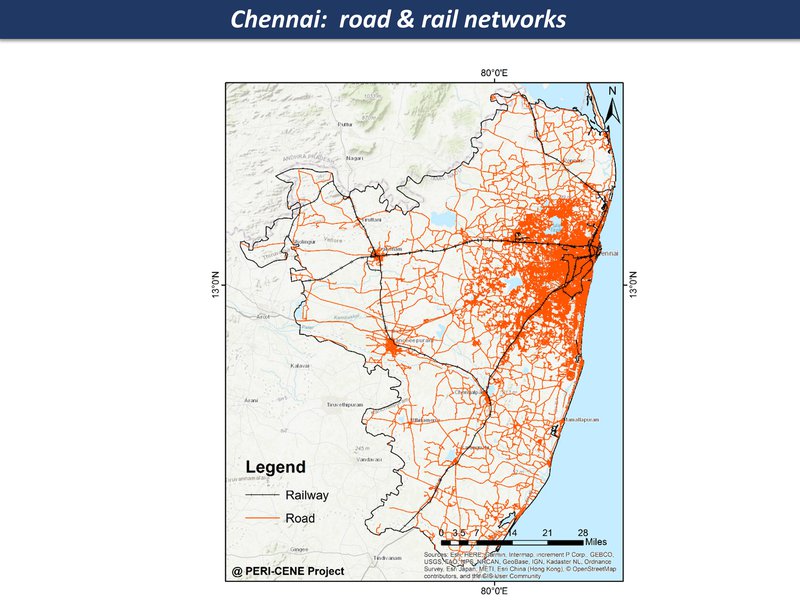
road & rail networks
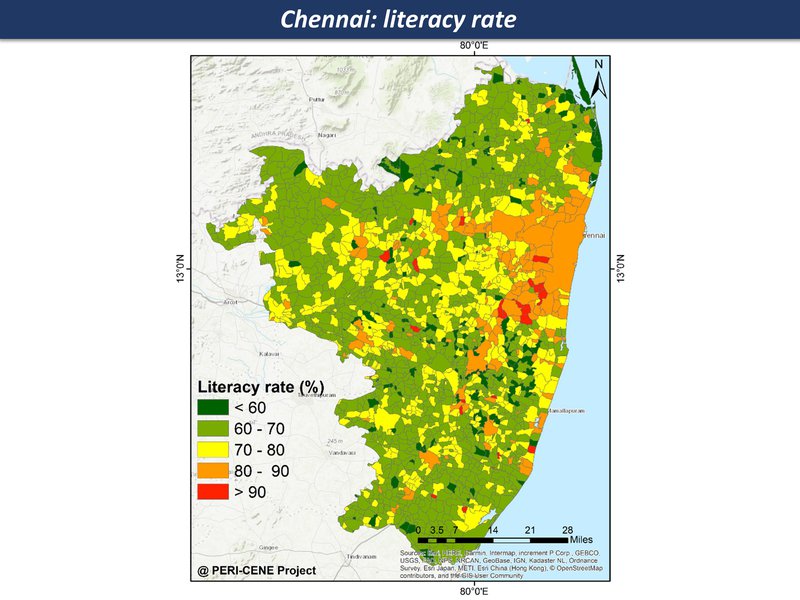
literacy rate
Chennai region overview
Chennai region overview
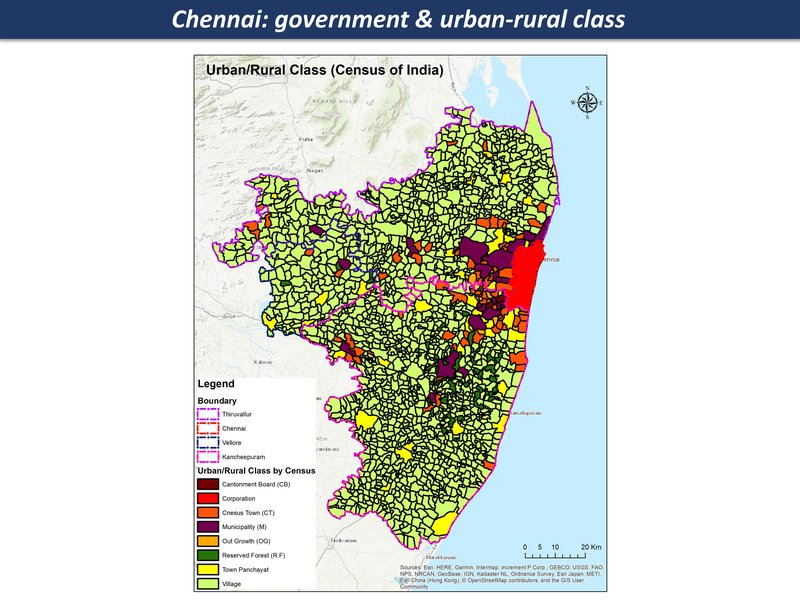
Quasi-government arrangements with industries, limited overview and regulation; mostly panchayat and local governance structures since there are many villages and small towns in this region
government & urban-rural class
Chennai region overview
Chennai region overview
opportunities for transformation - from a disrupted 'anti-eco-city-region' towards a post-industrial eco-region
Zone (b)
Chennai - Industrial corridor
Major highways criss-crossing industrial hubs and gated communities interspersed with farmlands and water bodies
Planned industrial/manufacturing hubs (Special economic zones), colleges and residential schools close to major highways leaving Chennai, unplanned flats (gated communities) and plotted housing, interspersed with villages, mid-sized towns, farming land and water bodies
Exponential growth in population in last two decades owing to SEZs and educational institutions; mixed housing options (low, middle and upscale), agricultural land converted to housing plots and other public infrastructure; manufacturing hubs with global investors in automobile, engineering and chemical industries, small town economies and mixed farming; speculative real estate,
very mixed - ranging from rural to upper-middle class lifestyles with global aspirations, income security, education, proximity to basic services etc; farming landscape with intricate network of connected water bodies in different levels of decline due to planned and unplanned changes in landscape
undercurrent tensions between local, global and governing bodies in the region over shared resources (land, water, employment opportunities) resulting in pastiche of formal and informal processes, new hierarchies; planned hub-and-spoke model through well-connecter corridors to the city failed to take off but resulted in corridor-centric growth
Zone (b)
Chennai - Industrial corridor
Extreme rainfall events triggering floods and droughts and subsequent impacts on land, biodiversity
Extreme rainfall events triggering floods and droughts and subsequent impacts on land, biodiversity
degraded water bodies leading to floods.waterlogging
complex waterscape - connected waterbodies of different sizes, rivers, reservoirs that feed the city; small to medium-scale farming still practised but in decline owing to changing lands and rainfall patterns;
rapid expansion in motor traffice & road infrastructure with CO2 emissions and air pollution
Zone (b)
Chennai - Industrial corridor
Fringe villages and towns adjacent to water bodies at higher levels of risk from flooding;
land affected by changing rainfall patterns and land-use patterns; west-to-east gentle slope that allows water to flow from one waterbody to another; mixed land-use
land affected by changing rainfall patterns and land-use patterns; west-to-east gentle slope that allows water to flow from one waterbody to another; mixed land-use
Fringe villages and towns adjacent to water bodies at higher levels of risk from flooding; gated communities and planned housing also at risk but lesser exposure to loss of livelihoods and can access bank savings (some contingency measures)
Most new housing projects sold on the promise of proximity and access to services, emergency care, schools etc but isolated during the floods of 2015; resilience to disasters is a mixed picture, can depend on social capital and other related factors
Zone (b)
Chennai - Industrial corridor
pockets of civil society action and local innovation could trigger pathways of transformation
SEZ act allowed large-scale conversion of land with many layers of informality built into it; enforcement and extent of pollution control on industries unclear with many polluted water bodies and ecosystems; rampant real estate speculation, plotted developments across the region
awareness of importance of water bodies amongst farmers leading to local protests, however limited mobilisation of local groups; NGO’s working on conservation of water bodies especially post-floods in critically affected areas
consistent conversion of land from agricultural to industrial, commercial, housing etc. complex web of land brokers, real-estate investors, local political heavyweights enabling this conversion process
pockets of civil society action and local innovation could trigger pathways of transformation
Zone (b)
Chennai - Industrial corridor
Growing pressure on fragile landscapes & settlements: potential for socio-eco-resilience
Special economic zones/rapid urbanisation
breakdown of fragile ecosystems unable to cope with climatic stress
Synergies of ecosystems & social systems: new semi-rural livelihoods: digital solution to fringe location
integrated adaptive upland landscapes: agro-forestry & eco-social innovation: innovative urban / building design for unstable & high risk locations