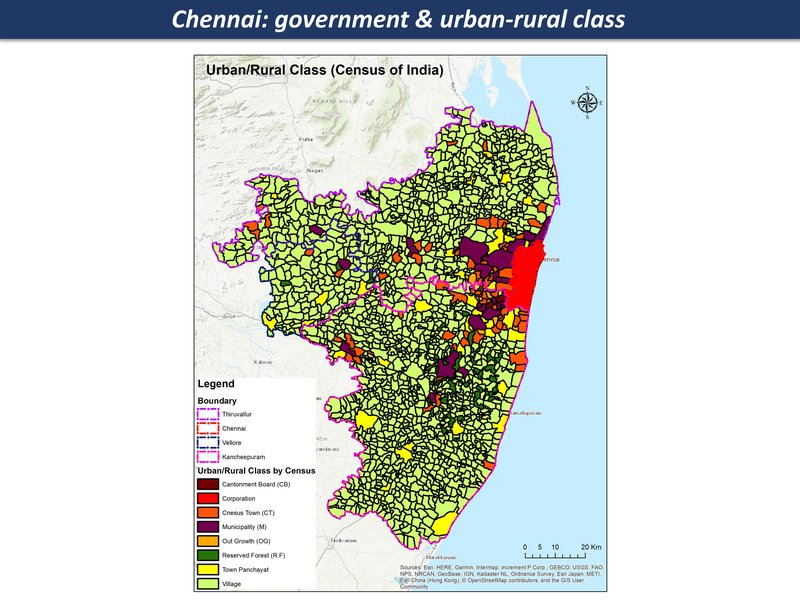
Chennai region
Peri-urban types & zones
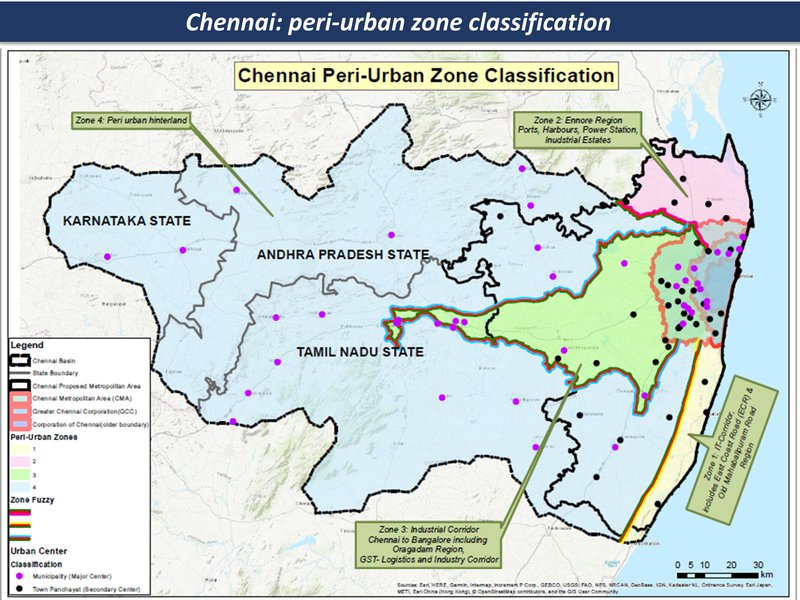
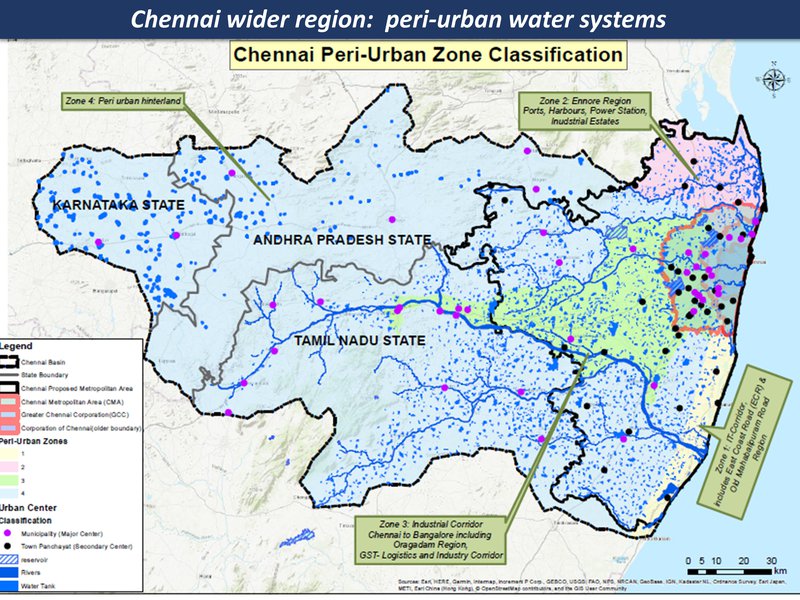
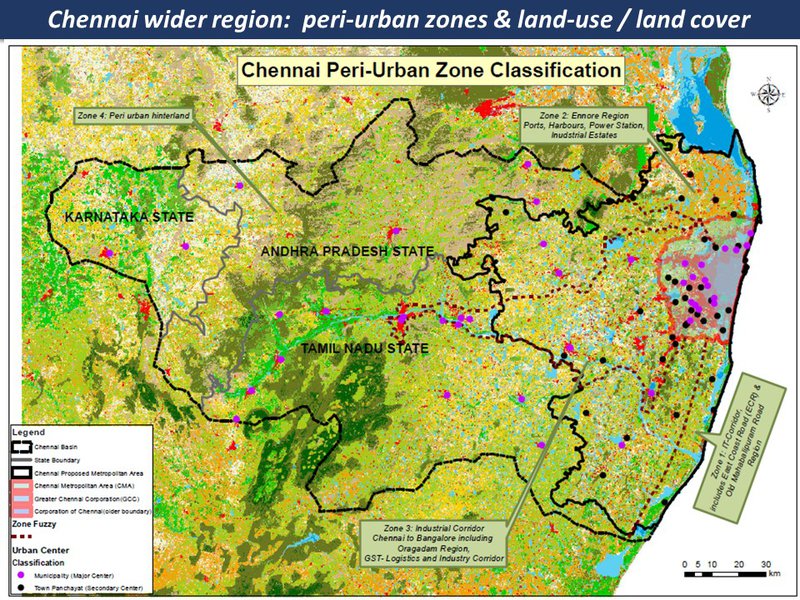
The peri-urban around Chennai is mapped here in four main zones, as on the following pages:
(A) Ennore & Thiruvallur
to the north of Chennai is a heavy-industries complex along the ecologically-degraded coastline, amid scattered towns and farmlands. The threats are from multiple climate change pressures, intersecting with a complex and problematic urban expansion. The opportunities are for a transition - from an eco-urban chaos to a post-industrial eco-region...
(B) Industrial corridor
includes the expansion of the metropolitan area in the direction of Bangalore. The landscape is one of major highways criss-crossing industrial hubs, and gated communities interspersed with local villages and farmlands, and the ancient system of water bodies now at risk.
(C) I.T. corridor
This area covers the southern coastal-to-hinterland landscape, with hi-tech industrial and entertainment / scenic / tourist corridors, interspersed with fishing villages, salt pans and small-scale farming
(D) Hinterland
The Chennai hinterland area includes a large watershed, with mid-sized cities, villages and farmlands and small-medium scale industries. (This area overlaps 3 states: Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh)
.
.
.
.
Overview of peri-urbanization and climate risks / adaptation
The Chennai case is large and complex.... here we show the summary of the Peri-cene Framework to illustrate the differences between the four zones. The following pages have more detail on each of the '20 questions' in the Framework.
Chennai region overview of zones
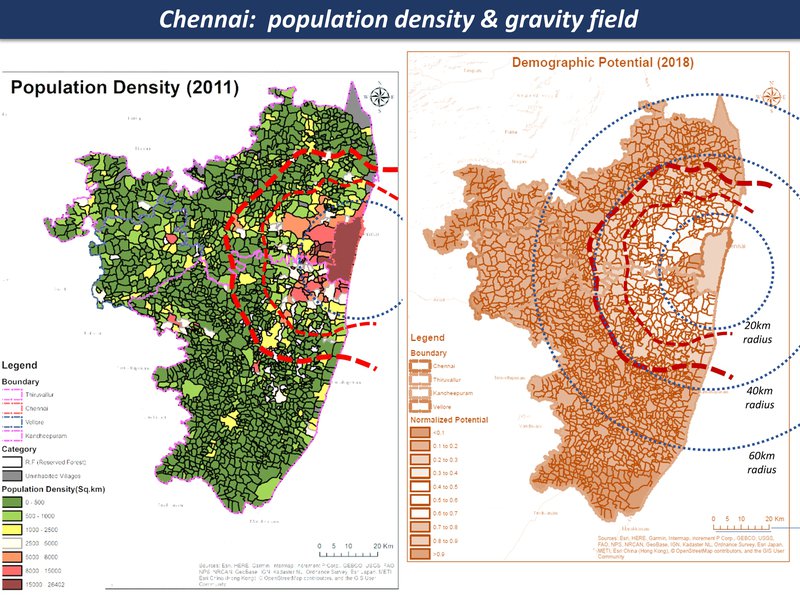
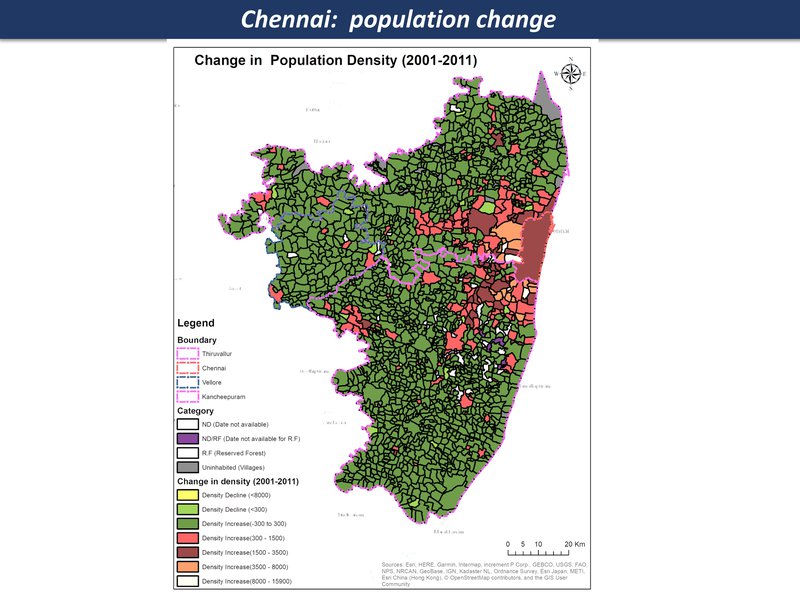
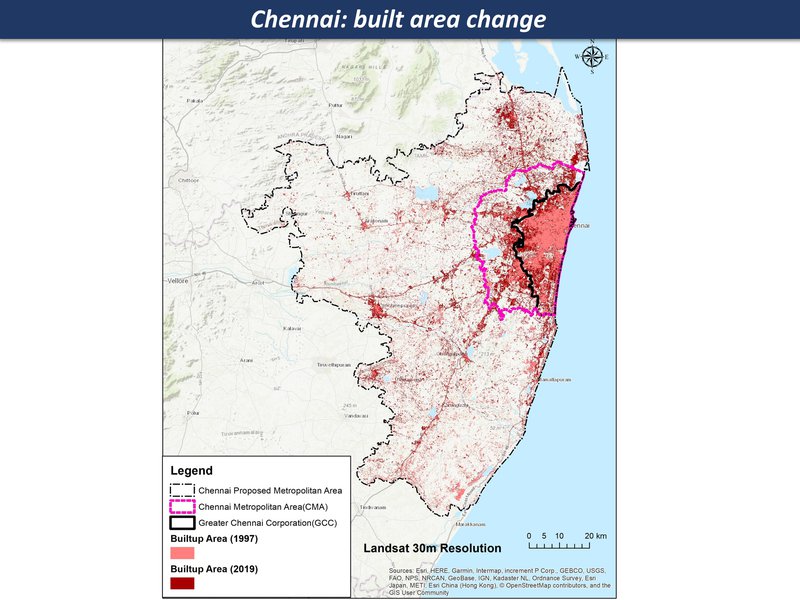
Overview with spatial analysis
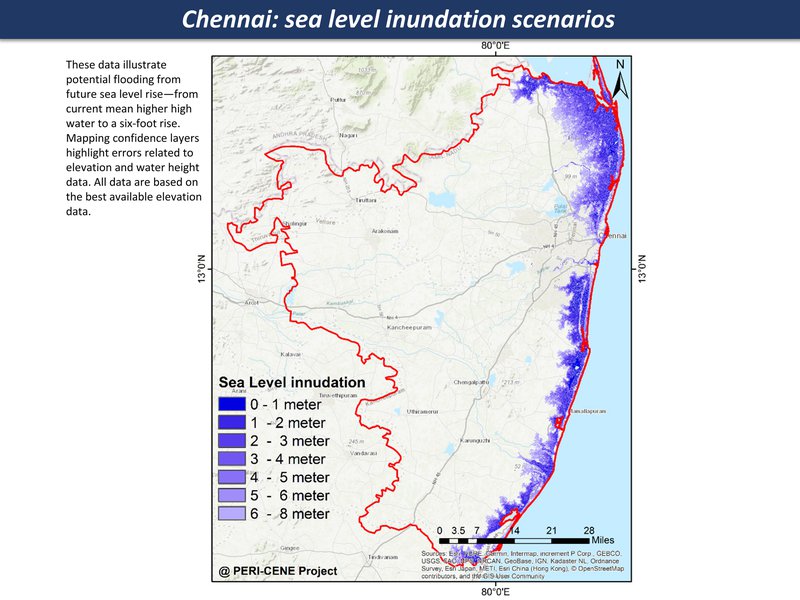
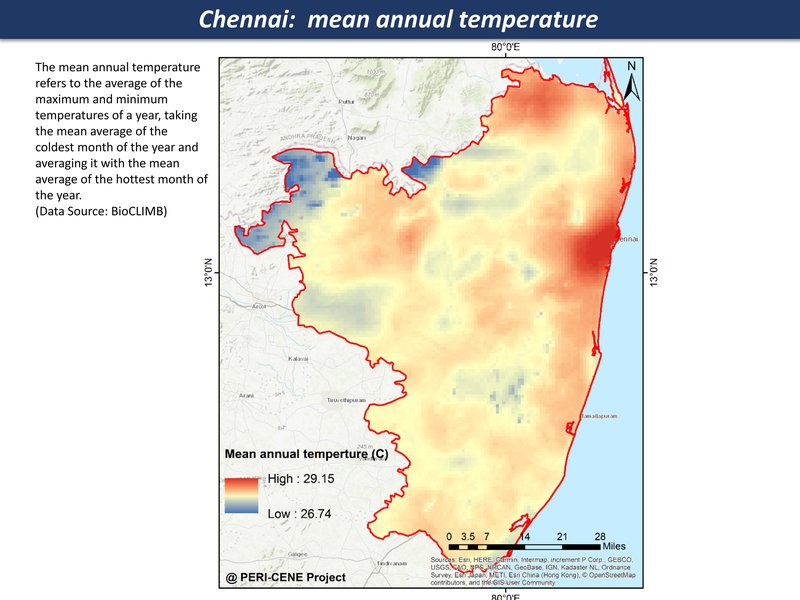
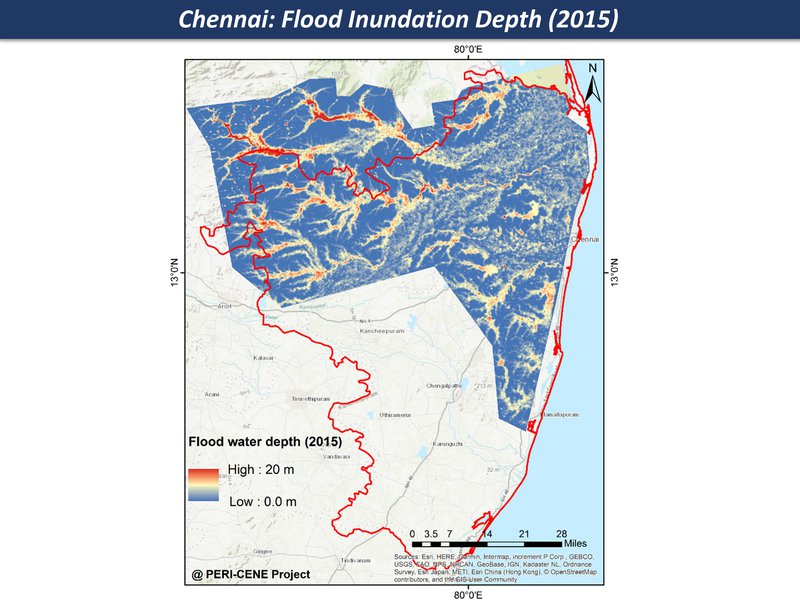
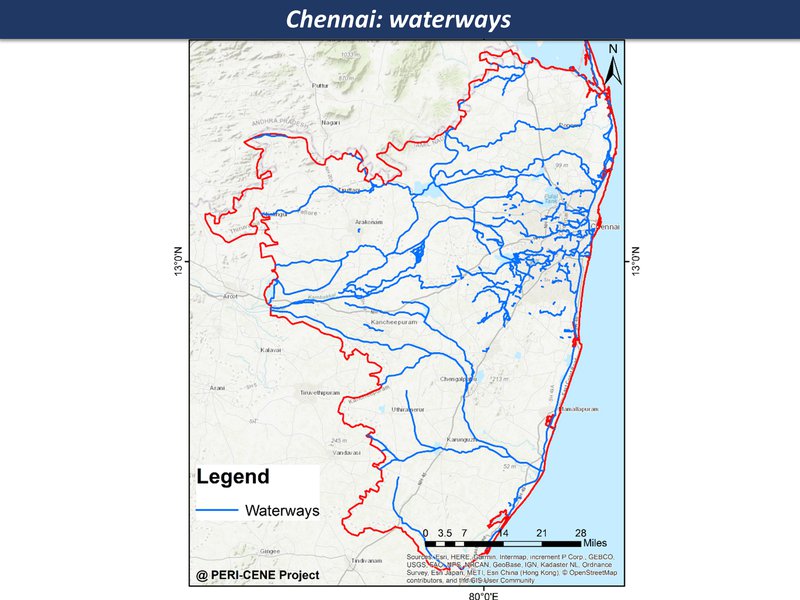
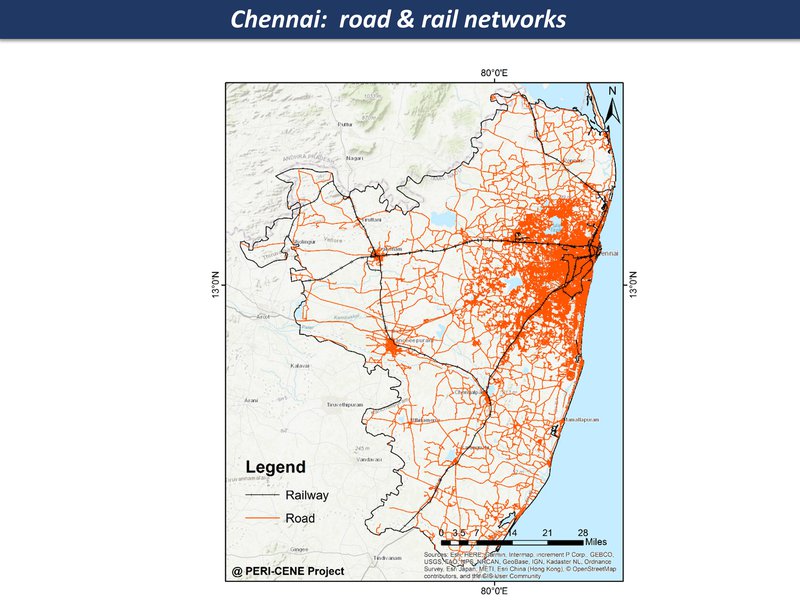
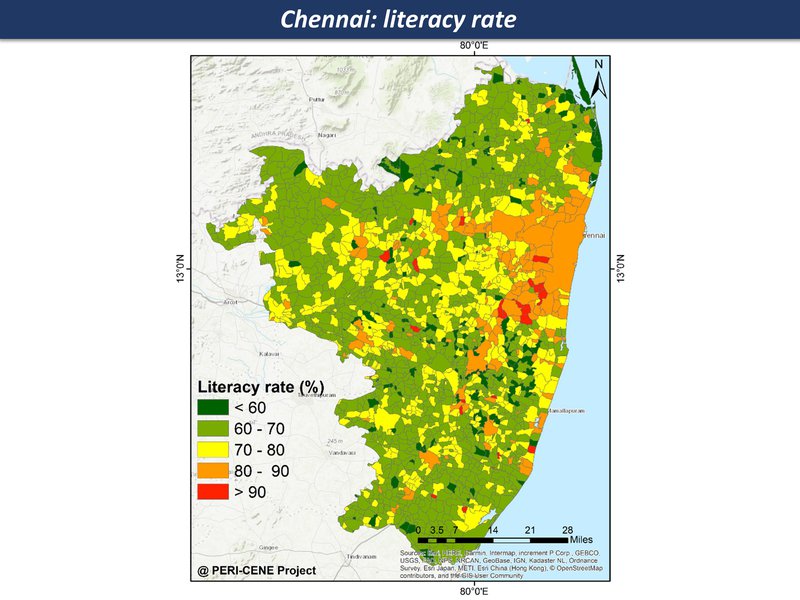
While the maps can't tell us everything about a large and complex system, they are a good place to start a discussion, each one telling a kind of story. Here are the main maps for the Chennai region so far, as a thematic map compilation - a working 'Atlas of the peri-urban' (preliminary work in progress)
.
Peri-Urban
- Urban direct expansion
- Urban / rural fringe & gradient
- Counter-urbanization effect
- Urban agglomeration effect
- Population growth & housing
- Technology & infrastructure
- Economy & employment
- Real estate & markets
- Social demographics & lifestyle
- Environment & resources
- Policy & governance
- Culture & ethics
- Internal structures
- external interactions
- power dynamics
- challenges & conflicts
Climate Risk
- temperature
- precipitation, storm etc
- coastal effects
- wildfire, heatwave, drought,
- flood, storm, cyclone
- landslide, sea incursion etc,
- water resources
- farming & forestry
- energy & resources
- ecosystems & microclimates
- critical infrastructure
- CO2 emissions from energy
- GHG emissions from land-use
- Land-use & forestry change
- Carbon storage
Vulnerability
- Soil & vegetation
- Topography & stability
- Settlement form & structure
- technical & infrastructure
- Markets & value effects
- Employment & livelihoods
- Affluence / deprivation
- Education / communication
- Cultural issues
- Local government
- Public services & infrastructure
- Emergency services
- Civil & community
Governance
- Public Sector
- Private Sector
- Civic Sector
- Citizens etc
- Informal land-use, settlements
- Corruption & nepotism
- Social innovation & enterprise
- Social learning & collaboration
- Social co-creation & mobilization potential
- System transformation potential
Synergistics
- Main cross-cutting issues: e.g.
- Airport / port cities:
- Rural livelihoods:
- Informal development
- Critical themes: (STEEP): e.g.
- Social cohesion declines
- AI / IOT emerges
- Climate change accelerates
- Potential ideas, connections, opportunities
- Goals, objectives, targets for ways forward.